Have you ever wondered what makes some computer monitors burst with incredibly vivid colors and astonishing brightness, seemingly bringing images to life? While display technology constantly evolves, Quantum Dot technology stands out as a revolutionary advancement, transforming the visual experience on our screens. This article will thoroughly explain Quantum Dot technology in monitors, from how these tiny nanoparticles work to the remarkable benefits they offer, and how they stack up against other popular display technologies like OLED and traditional LCDs. Let’s delve into the science behind these captivating displays and discover why they might be the perfect choice for your next computer monitor.
What is Quantum Dot Technology?
Quantum Dot technology leverages the unique properties of microscopic semiconductor nanoparticles, known as quantum dots, to enhance display performance. These dots are incredibly small, typically ranging from 2 to 10 nanometers in size, and their diminutive scale allows them to exhibit quantum mechanical properties. When exposed to light, these quantum dots absorb energy and then re-emit it as light of a specific, highly precise color. The crucial aspect is that the color of the emitted light is directly determined by the size of the quantum dot itself. Larger dots emit light towards the red end of the spectrum, while smaller ones emit green light.
How Quantum Dots Work in Monitors
In most Quantum Dot monitors, these nanoparticles are integrated into a specialized film layer positioned in front of a blue LED backlight. When the blue light from the backlight passes through this film, the quantum dots are excited. They then efficiently convert some of the blue light into pure red and green light. The remaining blue light from the LED passes through unaltered. By combining these pure red, green, and blue light components, the display can achieve a much broader and more accurate spectrum of colors than traditional LCD panels. This sophisticated color conversion process leads to a “purer” white light source for the display, enabling a significant improvement in color saturation, accuracy, and overall brightness.
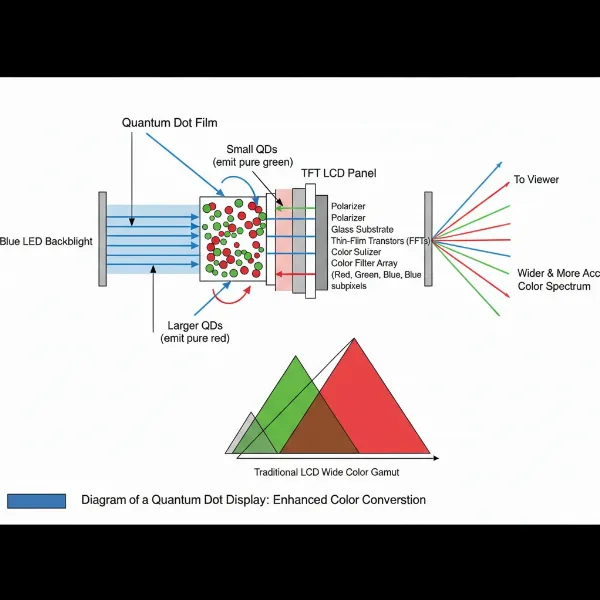 Diagram illustrating quantum dots converting blue light into pure red, green, and blue for a monitor display.
Diagram illustrating quantum dots converting blue light into pure red, green, and blue for a monitor display.
Types of Computer Monitor Technology
Understanding where Quantum Dot technology fits requires a brief look at the broader landscape of display types. Initially, most monitors relied on Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs), which themselves have evolved significantly.
Traditional LCD/LED Monitors
Traditional LCD monitors use a backlight (originally CCFL, now predominantly LED) to illuminate liquid crystals. These crystals act like tiny shutters, controlling how much light passes through them to create an image. Color filters are then used to produce red, green, and blue sub-pixels. While effective, this filtering process can lead to some light loss and limits the purity and range of colors achievable. Traditional LED-backlit LCDs form the foundation upon which Quantum Dot technology builds.
Quantum Dot LED (QLED) Monitors
QLED monitors are essentially enhanced LCD displays that incorporate a layer of quantum dots. By placing this quantum dot film between the LED backlight and the LCD panel, QLED technology dramatically improves color volume, brightness, and color accuracy compared to standard LED-backlit LCDs. The quantum dots precisely convert the blue backlight into a much wider spectrum of colors, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. This enhancement allows QLED monitors to achieve superior performance, especially when displaying High Dynamic Range (HDR) content.
 A QLED monitor displaying a vibrant, high-dynamic-range gaming scene with rich colors and brightness.
A QLED monitor displaying a vibrant, high-dynamic-range gaming scene with rich colors and brightness.
Quantum Dot OLED (QD-OLED) Monitors
A more recent innovation combines the strengths of Quantum Dots with Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) technology. QD-OLED monitors feature a blue OLED layer that acts as the light source. This blue light then excites a layer of quantum dots to produce red and green light. Unlike traditional OLEDs that use white subpixels and color filters, QD-OLED harnesses the precise color conversion of quantum dots to achieve incredibly pure and vibrant colors, while retaining OLED’s perfect blacks and individual pixel control. This hybrid approach aims to deliver the best of both worlds: OLED’s infinite contrast with Quantum Dot’s enhanced color purity and brightness.
Benefits of Quantum Dot Monitors
The integration of Quantum Dot technology brings a host of compelling advantages to computer monitors, significantly elevating the visual experience.
Unparalleled Color Accuracy and Wider Gamut
One of the most significant benefits of Quantum Dot technology is its ability to produce an incredibly wide and accurate color gamut. By emitting highly specific wavelengths of light, quantum dots enable displays to render colors with remarkable purity and precision. This translates to a broader spectrum of vibrant hues, often covering standards like 95% of the DCI-P3 color space or even 99% of Adobe RGB, which is crucial for professional content creators, graphic designers, and anyone who demands true-to-life color reproduction. The colors “pop” off the screen with an intensity that traditional displays simply cannot match.
Exceptional Brightness and HDR Performance
Quantum Dot displays are highly efficient at converting light, allowing them to achieve significantly higher peak brightness levels than many conventional monitors. This enhanced luminance is a game-changer for High Dynamic Range (HDR) content, where bright highlights and intricate details demand a display capable of expressing a wide range of light. With Quantum Dots, HDR content appears more impactful, creating a truly immersive viewing experience with stunning realism and depth. You’ll notice dazzling explosions, subtle glints of light, and vibrant outdoor scenes rendered with incredible fidelity.
 A close-up of a Quantum Dot monitor displaying a visually rich HDR landscape with bright highlights and deep colors.
A close-up of a Quantum Dot monitor displaying a visually rich HDR landscape with bright highlights and deep colors.
Enhanced Contrast and Deeper Blacks
While OLED technology is renowned for its perfect blacks, Quantum Dot technology also contributes to improved contrast ratios, particularly in QLED (LCD-based) monitors. By providing a purer and more controlled light source, quantum dots allow for better differentiation between light and dark areas on the screen. This results in images that have more depth and dimension, where details are preserved in both the brightest whites and the darkest shadows, enhancing overall picture quality.
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
The efficient light conversion process of quantum dots means that these displays can achieve impressive brightness levels with less power consumption compared to older display technologies. This energy efficiency not only benefits your electricity bill but also contributes to a longer lifespan for the display. Furthermore, Quantum Dot materials themselves are inorganic, which typically translates to greater stability and resistance to degradation over time, offering a more durable and lasting visual solution.
Quantum Dot Technology vs. Other Display Technologies
The choice between display technologies often comes down to a careful comparison of their strengths and weaknesses. Quantum Dot technology positions itself uniquely in this landscape.
Quantum Dot vs. Traditional LCD
The distinction here is clear: Quantum Dot technology acts as an enhancement for LCD panels. Traditional LCDs, even those with LED backlights, rely on color filters that inherently limit color purity and can result in light loss. Quantum Dot displays (QLEDs) overcome these limitations by using nanoparticles to create a highly optimized and broader spectrum of light. This fundamental difference means QLEDs offer significantly better color accuracy, wider color gamut, and higher brightness compared to their non-Quantum Dot LCD counterparts, providing a much more vibrant and immersive visual experience.
Quantum Dot vs. OLED
This is where the comparison becomes more nuanced, especially with the advent of QD-OLED.
- Brightness and Color Volume: QLED (Quantum Dot LCD) panels generally excel in peak brightness and color volume, especially in well-lit environments. Traditional OLEDs, while offering brilliant colors, historically couldn’t match the sheer brightness of QLEDs. QD-OLED, however, bridges this gap, combining OLED’s inherent advantages with Quantum Dot’s color and brightness enhancements, often achieving higher peak brightness than traditional OLEDs.
- Black Levels and Contrast: OLED technology remains the undisputed champion for black levels and contrast. Each pixel in an OLED display is self-emissive, meaning it can be individually turned off, resulting in “perfect black” and infinite contrast. QLED, being backlit, cannot achieve true perfect black, though local dimming technologies in high-end QLEDs can get remarkably close. QD-OLED maintains OLED’s perfect blacks while enhancing color performance.
- Viewing Angles: Traditional OLED displays offer exceptionally wide viewing angles with consistent color and contrast from almost any perspective. Some QLED (LCD-based) monitors might show slight color shifts or brightness degradation at extreme viewing angles due to the nature of LCD panels and their backlight. However, QD-OLED technology, benefiting from quantum dots, generally maintains excellent color and contrast consistency even at wide viewing angles.
- Burn-in Risk: One concern with traditional OLED technology is the potential for “burn-in” or permanent image retention, especially when static images are displayed for long periods. QLED monitors, being based on LCD technology with inorganic quantum dots, are not susceptible to burn-in. QD-OLED panels, while more resilient than older OLEDs, are still based on organic materials and thus still carry a theoretical, albeit reduced, risk of burn-in over extended periods of static content display.
“Quantum Dot technology has fundamentally redefined color reproduction and brightness capabilities in displays, pushing the boundaries of what consumers expect from their monitors.” – Dr. Evelyn Reed, Display Technology Analyst
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Quantum Dot Monitor
Selecting the right Quantum Dot monitor involves more than just understanding the technology; it requires aligning its capabilities with your specific needs.
Intended Use (Gaming, Content Creation, General Use)
Your primary use case will heavily influence your choice. For gaming, look for Quantum Dot monitors with high refresh rates (120Hz, 144Hz, 240Hz, or even 360Hz), low response times (1ms GTG or lower), and adaptive sync technologies like FreeSync or G-Sync. For content creation (graphic design, video editing), prioritize monitors with exceptional color accuracy, wide color gamut coverage (e.g., 99% Adobe RGB, 95%+ DCI-P3), and good factory calibration. For general use, a good balance of color, brightness, and resolution will suffice.
Panel Type (IPS, VA, TN) and QD Integration
While Quantum Dots enhance the color and brightness, the underlying LCD panel technology still plays a role:
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): Offers excellent color accuracy and wide viewing angles, making it a popular choice for Quantum Dot monitors, especially for creative work.
- VA (Vertical Alignment): Known for its high contrast ratios and deep blacks, often favored by gamers and movie watchers who prioritize immersive visuals.
- TN (Twisted Nematic): Historically known for very fast response times, though often at the expense of color accuracy and viewing angles. Less common in high-end Quantum Dot implementations.
When considering QD-OLED, the panel combines OLED’s self-emissive nature with Quantum Dot color conversion.
 A multi-monitor setup showcasing different uses like gaming, content creation, and general productivity.
A multi-monitor setup showcasing different uses like gaming, content creation, and general productivity.
Refresh Rate and Response Time
These are critical for a smooth visual experience, especially in fast-paced applications like gaming. Refresh rate (measured in Hz) indicates how many times per second the display updates its image. A higher refresh rate means smoother motion. Response time (measured in milliseconds) refers to how quickly pixels can change from one color to another. Lower response times reduce motion blur and ghosting. Many Quantum Dot monitors, particularly QD-OLEDs, offer exceptionally high refresh rates and ultra-low response times, making them ideal for competitive gaming.
HDR Support
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content thrives on displays with high peak brightness and wide color gamuts. Quantum Dot technology inherently supports and enhances HDR performance, delivering brighter highlights and more vibrant colors than standard dynamic range (SDR) content. Look for HDR certifications like DisplayHDR 400, 600, or 1000 for guaranteed performance levels.
Connectivity
Ensure the monitor offers the necessary ports for your devices. Common connections include HDMI (HDMI 2.0 or 2.1 for higher refresh rates and resolutions), DisplayPort (DisplayPort 1.4 or 2.1 for high bandwidth), and USB-C (for single-cable connectivity, power delivery, and video output). Additional USB hubs and KVM switches can also be convenient features.
Conclusion
Quantum Dot technology has undeniably pushed the boundaries of visual fidelity in Computer Monitors. By harnessing the precise light-emitting properties of nanoparticles, these displays deliver a stunning combination of expanded color gamuts, exceptional brightness, and remarkable color accuracy. Whether you opt for a QLED monitor that breathes new life into traditional LCDs or a cutting-edge QD-OLED that merges the best of both worlds, you’re investing in a display that provides a truly immersive and vibrant viewing experience. With superior HDR performance and the ability to cater to demanding tasks like gaming and professional content creation, Quantum Dot monitors represent a significant leap forward. Are you ready to witness your digital world in a new spectrum of brilliance?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between QLED and OLED?
QLED monitors use Quantum Dots to enhance an LED-backlit LCD panel, focusing on boosting brightness and color volume. OLED monitors, in contrast, feature self-emissive pixels that produce their own light, allowing for perfect blacks and infinite contrast. QD-OLED combines elements of both, using a blue OLED light source and Quantum Dots for color conversion to achieve both perfect blacks and expanded color.
Are Quantum Dot monitors good for gaming?
Absolutely. Quantum Dot monitors, especially modern QLED and QD-OLED models, are excellent for gaming. They offer wide color gamuts, high brightness (beneficial for HDR gaming), and often boast high refresh rates and low response times, providing a smooth, vibrant, and highly responsive gaming experience.
Do Quantum Dot monitors suffer from burn-in?
QLED monitors, which are based on LCD technology enhanced with Quantum Dots, are not susceptible to burn-in. However, QD-OLED monitors, which incorporate OLED elements, do carry a theoretical risk of burn-in, similar to traditional OLEDs, though advancements in panel technology and built-in preventative measures have significantly reduced this concern.
How does Quantum Dot technology improve color?
Quantum Dot technology improves color by using tiny nanoparticles that emit specific, pure wavelengths of red, green, or blue light when illuminated by a blue LED backlight. This process creates a much broader and more accurate color spectrum than traditional color filters in LCDs, resulting in more vivid, saturated, and true-to-life colors.
Is Quantum Dot technology energy efficient?
Yes, Quantum Dot technology can contribute to energy efficiency. The quantum dots are highly efficient at converting light, meaning they require less energy to achieve high brightness levels compared to older display technologies. This efficiency helps in producing vibrant images without excessive power consumption.
Can Quantum Dot technology display true black?
Quantum Dot LCD (QLED) monitors cannot display true black in the same way that self-emissive OLED pixels can, as they rely on a backlight. However, with advanced local dimming, QLEDs can achieve very deep blacks. QD-OLED displays, by incorporating OLED’s self-emissive properties, are capable of producing true, perfect blacks.