Screen tearing is a frustrating visual artifact that can shatter immersion and disrupt your gaming experience. It happens when your graphics card sends frames faster or slower than your monitor’s refresh rate, leading to horizontally misaligned images across your display. While V-Sync has long been the go-to solution for this problem, it comes with notorious drawbacks, primarily increased input lag and potential frame rate stuttering. Many gamers and professionals seek alternative methods to achieve smooth, tear-free visuals on their computer monitor without sacrificing responsiveness. This guide will explore effective V-Sync alternatives, helping you achieve perfect visual synchronization.
Understanding Screen Tearing and Why V-Sync Isn’t Always the Answer
Screen tearing is fundamentally a synchronization issue. Your graphics processing unit (GPU) renders frames at a variable rate, while your computer monitor refreshes its display at a fixed rate (e.g., 60Hz, 144Hz). When these rates don’t align, the monitor can display parts of two different frames simultaneously, resulting in a visible “tear” line. V-Sync (Vertical Synchronization) solves this by forcing the GPU to wait for the monitor’s refresh cycle before sending a new frame. This ensures that only complete frames are displayed, eliminating tearing.
However, V-Sync introduces its own set of problems. The GPU waiting for the monitor can cause a noticeable delay between your input and the on-screen action, known as input lag, which is detrimental in fast-paced games. If your frame rate drops below your monitor’s refresh rate, V-Sync might halve your FPS to the nearest multiple, leading to stuttering. For these reasons, many users actively seek ways to fix screen tearing without engaging V-Sync.
Leveraging Adaptive Sync Technologies: G-Sync and FreeSync
Adaptive Sync technologies, such as NVIDIA’s G-Sync and AMD’s FreeSync, revolutionized display synchronization by offering a dynamic solution to screen tearing. Unlike V-Sync, which forces the GPU to match the monitor, adaptive sync allows your computer monitor’s refresh rate to dynamically adjust and match the frame rate output by your GPU. This creates a seamlessly synchronized experience, eliminating tearing and reducing stuttering without the significant input lag associated with V-Sync.
For these technologies to work, both your graphics card and your computer monitor must be compatible. Once enabled, G-Sync or FreeSync monitors will adjust their refresh rate on the fly to perfectly align with your GPU’s output. To get the most out of adaptive sync and ensure tear-free visuals, it’s often recommended to cap your in-game frame rate slightly below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate. For example, if you have a 144Hz monitor, setting an FPS cap of 141-143 frames per second can ensure your GPU always stays within the adaptive sync range, preventing tearing that might occur if the frame rate exceeds the monitor’s capability. This slight adjustment ensures continuous synchronization, providing an incredibly smooth visual experience.
 A computer monitor displaying a game with no screen tearing, illustrating the effect of adaptive sync technology.
A computer monitor displaying a game with no screen tearing, illustrating the effect of adaptive sync technology.
Driver-Side Synchronization Features: NVIDIA Fast Sync and AMD Enhanced Sync
Beyond adaptive sync, both NVIDIA and AMD offer proprietary driver-level synchronization technologies that aim to reduce screen tearing with minimal input lag, serving as excellent V-Sync alternatives. These solutions work on a principle often referred to as “triple buffering” or a similar method that manages how frames are presented.
NVIDIA Fast Sync
NVIDIA Fast Sync is designed for scenarios where your GPU produces significantly more frames than your computer monitor’s refresh rate. Instead of discarding frames or making the GPU wait (like V-Sync), Fast Sync allows the GPU to render frames as fast as possible. It then intelligently selects and sends only the most recent complete frame to the monitor, effectively discarding older, already rendered frames that would lead to tearing. This approach significantly reduces tearing while maintaining very low input lag, making it ideal for competitive gaming where responsiveness is paramount. You can typically enable Fast Sync through the NVIDIA Control Panel under the “Manage 3D settings” section, either globally or for specific games.
AMD Enhanced Sync
AMD Enhanced Sync operates on a similar concept to NVIDIA’s Fast Sync. It’s an alternative V-Sync mode that aims to minimize both visual tearing and input lag without capping your frame rates. When your GPU renders frames faster than your monitor can display them, Enhanced Sync allows the GPU to send only the latest complete frame, dropping older frames. This ensures that you don’t experience tearing, and it prevents the stuttering associated with traditional V-Sync when frame rates drop. Enhanced Sync can be found and enabled within the AMD Radeon Software, typically under the “Gaming” -> “Graphics” settings, and can be applied globally or per-game. While it introduces an extremely small amount of input lag, for most users, it’s a negligible trade-off for tear-free gameplay.
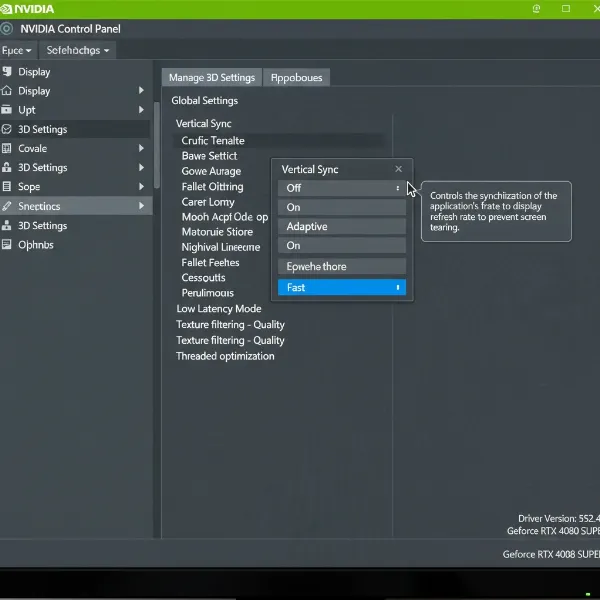 A screenshot of graphics driver settings for NVIDIA or AMD, showing where to enable Fast Sync or Enhanced Sync.
A screenshot of graphics driver settings for NVIDIA or AMD, showing where to enable Fast Sync or Enhanced Sync.
Software-Based Frame Rate Limiting and Display Adjustments
Sometimes, the most effective way to combat screen tearing without V-Sync involves more direct control over your frame rate and display settings. These software-based methods can provide excellent results, especially when adaptive sync is not an option or when dealing with specific game behaviors.
Implementing an FPS Cap with RivaTuner Statistics Server (RTSS)
One highly effective method is to cap your frame rate using third-party software like RivaTuner Statistics Server (RTSS). RTSS is a popular utility that allows you to set a precise frame rate limit for any game or application. By setting an FPS cap that is equal to or slightly below your computer monitor’s refresh rate, you can ensure that your GPU never exceeds the monitor’s drawing capability. This consistency can dramatically reduce or even eliminate screen tearing. It’s particularly useful if you find your GPU is consistently rendering frames well above your monitor’s refresh rate, as it prevents the desynchronization that causes tearing. Download RTSS, launch it, add your game, and set the desired frame rate limit.
Optimizing with Borderless Windowed Mode
Playing games in borderless windowed mode can often implicitly resolve screen tearing issues. Operating systems typically apply a form of triple buffering to windowed applications, which helps to synchronize frame presentation. In this mode, the desktop compositor manages how frames are displayed, often resulting in less tearing compared to exclusive fullscreen mode, even without V-Sync enabled. The main advantages are the reduction in tearing and the convenience of quickly switching between applications without minimizing your game. However, a potential downside is a slight performance overhead compared to exclusive fullscreen, as the operating system has to do additional work managing the desktop and application windows.
Manually Matching Monitor Refresh Rate
For certain games or systems, especially those where your frame rate is consistently stable but lower than your monitor’s maximum refresh rate, you might consider manually adjusting your computer monitor’s refresh rate. If your game consistently runs at, say, 75 FPS, and your monitor supports it, you could set your monitor’s refresh rate to 75Hz. This direct match ensures that for every frame your GPU produces, your monitor is ready to display it, significantly reducing tearing. This method requires your game’s frame rate to be stable and your monitor to support the desired refresh rate. You can usually change your monitor’s refresh rate through your operating system’s display settings.
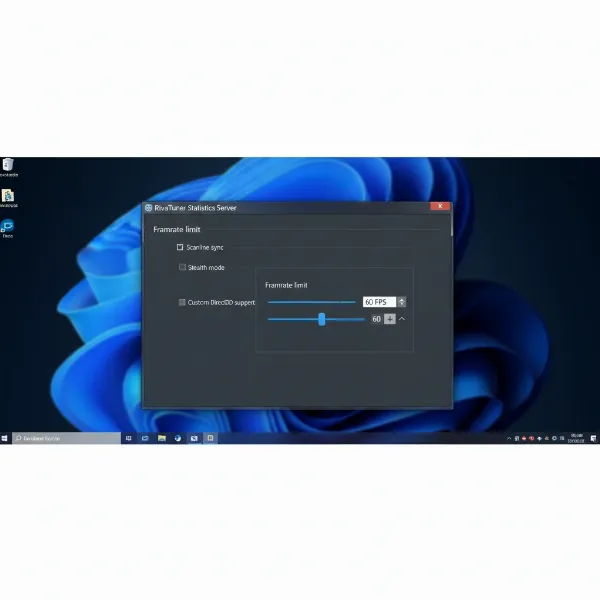 A graphical user interface of an FPS limiting software like RTSS, showing an FPS cap set.
A graphical user interface of an FPS limiting software like RTSS, showing an FPS cap set.
Advanced Considerations and Troubleshooting for Your Computer Monitor
Achieving a truly tear-free experience without V-Sync often involves more than just a single setting. Here are some advanced tips to consider:
- Keep Your Drivers Updated: Always ensure your graphics card drivers are up to date. Manufacturers frequently release updates that improve performance, add new features, and refine synchronization technologies. Outdated drivers can lead to unexpected visual glitches, including tearing.
- Experiment with Settings: There is no universal “magic bullet” solution that works perfectly for every game and every hardware configuration. What works best for one game might not be optimal for another. Be prepared to experiment with different combinations of settings within your game, graphics drivers, and operating system.
- Hardware Compatibility: For adaptive sync technologies like G-Sync and FreeSync, make sure your computer monitor and GPU are fully compatible. Not all monitors or graphics cards support these features. Check your product specifications to confirm compatibility.
- Understanding Input Lag: While minimizing screen tearing is important, competitive players often prioritize the lowest possible input lag. Methods like Fast Sync and Enhanced Sync are designed to minimize this, but all synchronization methods will introduce some degree of latency, however small. Finding the right balance for your personal preference and game type is crucial.
Comparison of V-Sync Alternatives
To help you decide which method is best for your computer monitor setup, here’s a comparison of the various tearing reduction techniques:
| Feature | V-Sync | G-Sync/FreeSync | Fast Sync/Enhanced Sync | Software FPS Cap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tearing Reduction | High (at cost) | Excellent (within range) | High | Good (with stable FPS) |
| Input Lag | High | Very Low | Very Low | Low |
| Performance Impact | FPS capped to refresh rate | Minimal (within range) | Minimal | Can reduce stutter |
| Hardware Required | None | Compatible Monitor & GPU | NVIDIA/AMD GPU | Software |
| Best Use Case | Last resort | Gaming, high refresh | Competitive gaming | Stable FPS games |
Finding the Right Solution for Your Computer Monitor Setup
Determining the best method to fix screen tearing without V-Sync depends heavily on your specific computer monitor setup, your graphics card, and your personal preferences. Start by assessing your hardware: Do you have an NVIDIA or AMD GPU? Does your monitor support G-Sync or FreeSync? If so, adaptive sync technologies are often the most robust and recommended solution.
If adaptive sync isn’t an option, or if you encounter issues, explore driver-side solutions like NVIDIA Fast Sync or AMD Enhanced Sync. For those seeking even finer control or dealing with particular games, a software-based FPS cap using tools like RTSS, combined with borderless windowed mode, can be highly effective. The best approach is often a combination of methods tailored to specific games and your hardware. Don’t be afraid to experiment to find the optimal balance between tear-free visuals and minimal input lag.
“Screen tearing can be incredibly distracting, but modern technologies and clever software solutions offer excellent ways to achieve smooth, tear-free visuals without the traditional pitfalls of V-Sync. The key is to understand your hardware and experiment with the options available to you.” – Dr. Elena Petrova, Lead Display Engineer at TechVision Labs
Conclusion
Eliminating screen tearing on your computer monitor without resorting to V-Sync is not only possible but increasingly straightforward with the advancements in display technology and software. Whether you leverage the dynamic synchronization of G-Sync or FreeSync, the intelligent frame management of NVIDIA Fast Sync or AMD Enhanced Sync, or precise frame rate capping with tools like RTSS, you have a wealth of options at your disposal. Each method offers a unique balance of tear reduction, input lag, and performance, allowing you to tailor your solution to your specific hardware and gaming preferences. By understanding these alternatives, you can enjoy a consistently smooth, visually stunning experience without the compromises of traditional V-Sync. Which method will you try first to achieve perfect visuals on your computer monitor?
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes screen tearing on a computer monitor?
Screen tearing occurs when your graphics card renders frames faster or slower than your computer monitor’s refresh rate, causing the monitor to display parts of multiple frames simultaneously, resulting in a “tear” across the screen. This desynchronization breaks the continuity of the image.
Is adaptive sync (G-Sync/FreeSync) better than V-Sync?
Generally, yes. Adaptive Sync technologies offer superior image fluidity and reduced input lag compared to traditional V-Sync. They dynamically synchronize your Computer Monitor’s refresh rate with your GPU’s frame rate, eliminating tearing without the performance penalties or input delay V-Sync can introduce.
Can I completely eliminate screen tearing without any sync technology?
While adaptive sync offers the most robust solution, you can significantly reduce or eliminate screen tearing without V-Sync by using driver-side solutions like NVIDIA Fast Sync or AMD Enhanced Sync, implementing a precise frame rate cap, or playing in borderless windowed mode. However, these methods might not offer a 100% tear-free experience in all scenarios without some form of synchronization, especially in highly fluctuating frame rate situations.
